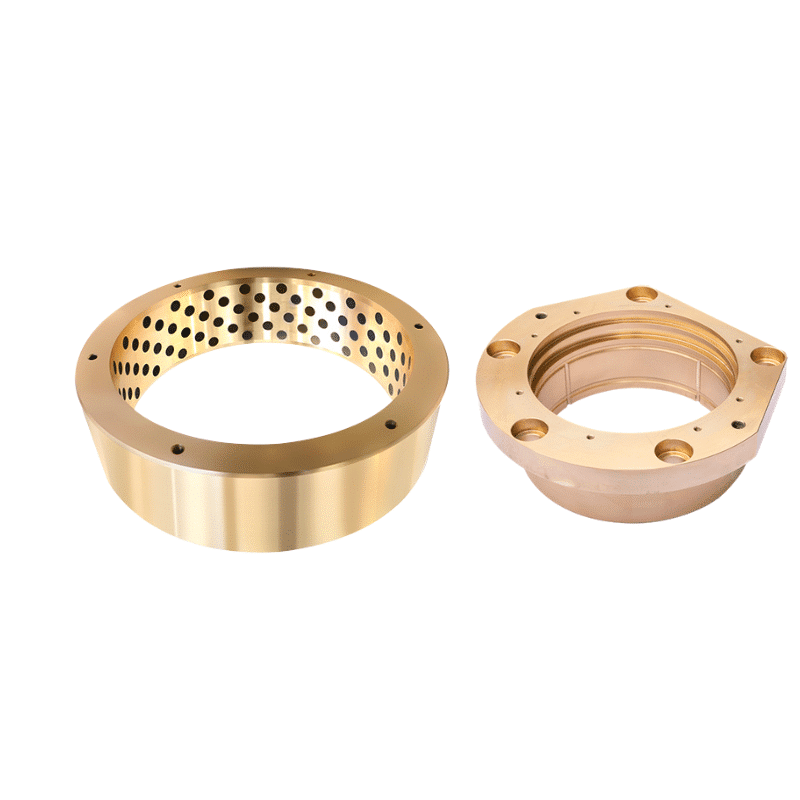
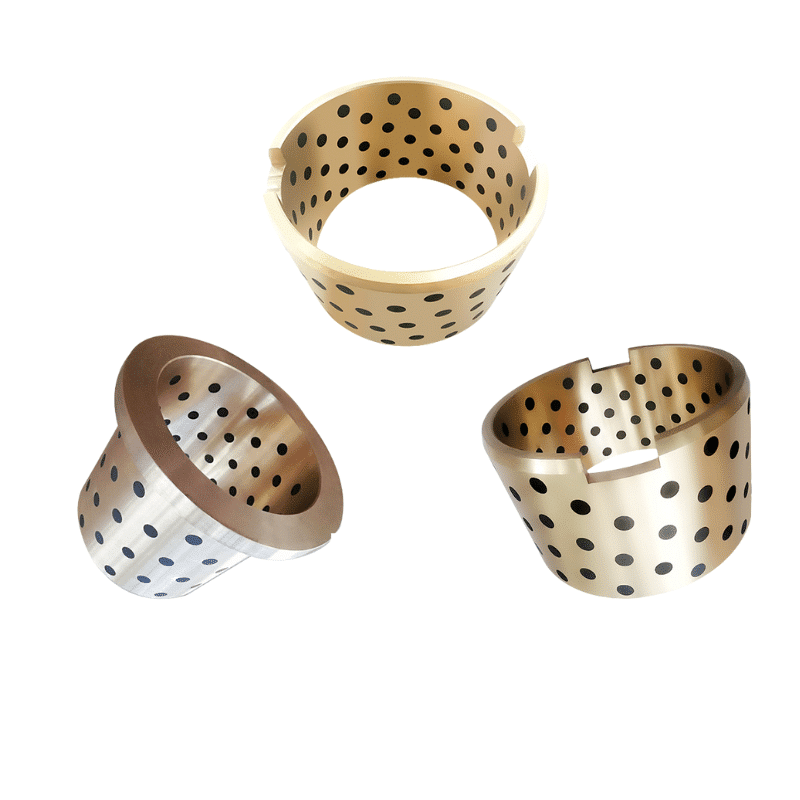
Cast Bronze Plate
Cast Bronze Plate
Say goodbye to the hassle of frequent lubrication maintenance. Our self-lubricating technology ensures smooth operation and reduces wear and tear, extending the lifespan of your equipment. Experience uninterrupted productivity and cost savings as you bid farewell to the need for messy lubricants and time-consuming upkeep.
Manufacturing on Demand
Cast Bronze Plate
Explore our selection of 954 Aluminum Bronze products, featuring premium-quality 954 bronze available in a variety of forms such as wear plates, solid plates, bronze bearing rings, and castings.
When it comes to sourcing or manufacturing Brass, Bronze Plate, Copper Alloys, and Cast Bronze Bars, it is important to focus on quality and precision. These materials are used in various industries due to their excellent mechanical properties and high corrosion resistance.
Oiles 500 material plate bearing
Brass Plate & Copper Alloys: These materials are typically used for their electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal. They can be found in applications such as electrical components, decorative items, and heat exchangers. The copper alloys can include a variety of elements, such as zinc (to form brass), tin (to form bronze), nickel, and others, each imparting specific properties to the alloy.
Bronze Plate: Bronze plates are made primarily from copper and tin but can also include other elements such as phosphorus, aluminum, and manganese. They are known for their high strength, resistance to wear, and excellent machining properties. They are used in applications such as bushings, bearings, and other heavy-duty mechanical parts.
Cast Bronze Bar Stock: This material is made through a process called continuous casting or centrifugal casting. The casting process allows for consistent composition and properties throughout the material, making it suitable for precision parts. It’s often used in applications that require high strength, good wear resistance, and excellent machinability, such as gears, bushings, and bearings.
Precision Bronze Plate: Precision bronze plates are manufactured to high dimensional accuracy and surface finish. They are used in applications where precise shapes and sizes are crucial, such as in the aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries.
Regardless of the type of material, quality control is a critical aspect of the production process. This can include chemical analysis to ensure correct alloy composition, mechanical property testing, and dimensional inspections.
Manufacturing the C51900 brass sleeve for port machinery using the horizontal continuous casting copper guide involves several stages:
- Raw Material Selection: The process starts with the selection of C51900 brass, an alloy containing copper and tin. This alloy is chosen for its strength, wear resistance, and excellent machinability, making it suitable for applications like port machinery sleeves.
- Melting: The raw materials are melted in a furnace at temperatures typically ranging from 1,000 to 1,100 degrees Celsius. Impurities that float to the surface of the molten metal are removed.
- Casting: The molten brass is then transferred to the horizontal continuous casting machine. This machine includes a water-cooled mold that shapes the molten brass into a long, horizontal bar. As the brass solidifies, it’s continuously pulled through the machine. This allows for efficient, high-volume production of brass bars with consistent cross-sectional shape and size.
- Cooling: After casting, the brass bars are cooled slowly to room temperature. This helps to prevent the formation of internal stresses that could potentially weaken the material.
- Machining: The cooled brass bars are machined into sleeves. This involves processes such as turning, drilling, and milling, which are used to achieve the precise dimensions and surface finish required for the port machinery application.
- Quality Control: After machining, the brass sleeves are inspected and tested to ensure they meet the required specifications. This may include measurements of dimensions, hardness testing, and potentially non-destructive testing methods to check for internal defects.
- Packaging and Shipment: Once the quality control checks are completed, the sleeves are packaged and prepared for shipment to the customer or end user.
The key advantage of using horizontal continuous casting for brass sleeve production is that it enables efficient, high-volume production, while also ensuring consistent product quality. It’s a widely used method in the manufacture of a variety of copper alloy products, including those made from C51900 brass.
Bronze Plate Material
Below is the translated version of the Cast Copper Alloy Mechanical Properties Chart:
| Alloy Name | Alloy Grade | Mechanical Properties ≥ | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength σb/MPa | Yield Strength σ0.2/MPa | Elongation δ5% | Brinell Hardness (HB) | ||
| Tin Bronze 555 | ZCu5Pb5Zn5 | 200 | 90 | 13 | 590 |
| Tin Bronze 10-1 | ZCu10P1 | 220 | 130 | 3 | 785 |
| Tin Bronze 10-5 | ZCuSn10Pb5 | 195 | – | 10 | 685 |
| Tin Bronze 10-2 | ZCuSn10Pb2 | 240 | 120 | 12 | 685 |
| Aluminum Bronze 8-13-3 | ZCuA118Mn13Fe3 | 600 | 270 | 15 | 1570 |
| Aluminum Bronze 9-2 | ZCuA19Mn2 | 390 | – | 20 | 835 |
| Aluminum Bronze 9-4-4-2 | ZCuA19Fe4Ni4Mn2 | 630 | 250 | 16 | 1570 |
| Aluminum Bronze 10-3 | ZCuA110Fe3 | 490 | 180 | 13 | 980 |
| Aluminum Bronze 10-3-2 | ZCuA110Fe3Mn2 | 490 | – | 15 | 1080 |
| Brass H62 | ZCuZn38 | 295 | – | 30 | 590 |
| Aluminum Brass 25-6-3-3 | ZCuZn25A16Fe3Mn3 | 725 | 380 | 10 | 1570 |
| Manganese Brass 38-2-2 | ZCuZn38Mn2Pb2 | 245 | – | 10 | 685 |
Note: Brinell hardness test, the unit of force is Newton (N); Cast Copper Alloy Mechanical Properties Table
When it comes to producing bronze plates, bushings, liners, washers, and wear plates, it’s essential to understand the different ASTM standards, material grades, and manufacturing processes involved.
- Bronze Plate – Quick, Finished & Machined: These plates are quickly produced, finished, and machined to meet specific application requirements. The precision machining process ensures that the final product meets exact size, shape, and surface finish requirements.
- Centrifugally Cast: This process involves pouring molten bronze into a spinning mold. The centrifugal force pushes the molten bronze against the wall of the mold, resulting in a component with a fine grain structure, excellent mechanical properties, and high durability.
- Custom Machined Bronze Bushings, Liners, Washers, Wear Plates: These components are custom machined from the centrifugally cast bronze to meet the specific needs of various applications. They can be found in a wide range of machinery and equipment, offering excellent load-bearing capabilities, wear resistance, and long service life.
- Material Standards:
- SAE 64: This is a leaded tin bronze alloy that offers good machinability, reasonable strength and wear resistance. It’s often used in moderate load applications.
- ASTM B143: This specification covers the requirements for continuous cast and ingot cast tin bronze alloys for industrial applications.
- ASTM B271: This standard specifies requirements for copper-base alloy centrifugal castings.
- ASTM B505: This standard outlines the requirements for continuous cast copper and copper-alloy products.
- ASTM B584: This standard covers requirements for copper alloy sand castings for general applications.
- QQ-C-390: This federal specification covers the requirements for copper-alloy die castings.
- Lead: Lead is often added to bronze alloys to increase their machinability. The lead creates tiny inclusions in the metal that act as chip breakers during machining, allowing the metal to be cut more easily and with a smoother finish.
The use of the appropriate manufacturing methods, material grades, and standards is critical in achieving the desired mechanical properties and ensuring that the final product meets the requirements of its intended application.
The production of bronze products can be achieved using several casting methods, each offering unique advantages depending on the product’s requirements. The following are brief descriptions of these methods:
- Centrifugal Castings: In centrifugal casting, the molten bronze is poured into a rotating mold. The centrifugal force pushes the material towards the mold walls and promotes the formation of a part with a dense, uniform structure, free from gas porosity and impurities that are normally driven towards the center. This process is often used for cylindrical-shaped objects like pipes, bushings, or rings, and it yields high-quality products with excellent mechanical properties.
- Continuous Castings: Continuous casting, as the name suggests, is a continuous process where molten bronze is poured into a mold which moves continuously. The solidified product comes out from the other end of the mold in the desired cross-sectional shape and size (like rods, bars, tubes, etc.). This process provides consistent chemical composition and mechanical properties throughout the length of the casting. It’s a cost-effective process for high-volume production.
- Sand Castings: In sand casting, a sand mold is formed around a pattern that resembles the final product. The molten bronze is then poured into the mold. Once the bronze solidifies, the sand mold is broken away. This method is versatile and can be used to produce a wide range of shapes and sizes, including complex geometries. It is relatively economical for small to medium batch sizes.
Regardless of the casting method chosen, each product can be manufactured to your specifications. This includes factors such as the type of bronze alloy used, the dimensions of the final product, and any post-processing requirements (e.g., heat treatment, machining, surface finish, etc.).
To ensure that products meet your specifications, rigorous quality control measures are usually implemented. These can include checks for dimensional accuracy, tests for mechanical properties (such as strength and hardness), and inspections for defects or imperfections. The goal is to ensure that each bronze product meets the highest quality standards and is fit for its intended application.
The production of bronze products can be achieved using several casting methods, each offering unique advantages depending on the product’s requirements. The following are brief descriptions of these methods:
- Centrifugal Castings: In centrifugal casting, the molten bronze is poured into a rotating mold. The centrifugal force pushes the material towards the mold walls and promotes the formation of a part with a dense, uniform structure, free from gas porosity and impurities that are normally driven towards the center. This process is often used for cylindrical-shaped objects like pipes, bushings, or rings, and it yields high-quality products with excellent mechanical properties.
- Continuous Castings: Continuous casting, as the name suggests, is a continuous process where molten bronze is poured into a mold which moves continuously. The solidified product comes out from the other end of the mold in the desired cross-sectional shape and size (like rods, bars, tubes, etc.). This process provides consistent chemical composition and mechanical properties throughout the length of the casting. It’s a cost-effective process for high-volume production.
- Sand Castings: In sand casting, a sand mold is formed around a pattern that resembles the final product. The molten bronze is then poured into the mold. Once the bronze solidifies, the sand mold is broken away. This method is versatile and can be used to produce a wide range of shapes and sizes, including complex geometries. It is relatively economical for small to medium batch sizes.
Regardless of the casting method chosen, each product can be manufactured to your specifications. This includes factors such as the type of bronze alloy used, the dimensions of the final product, and any post-processing requirements (e.g., heat treatment, machining, surface finish, etc.).
To ensure that products meet your specifications, rigorous quality control measures are usually implemented. These can include checks for dimensional accuracy, tests for mechanical properties (such as strength and hardness), and inspections for defects or imperfections. The goal is to ensure that each bronze product meets the highest quality standards and is fit for its intended application.
Your expert in self-lubricating Bearing
and Bronze alloys – serving globally