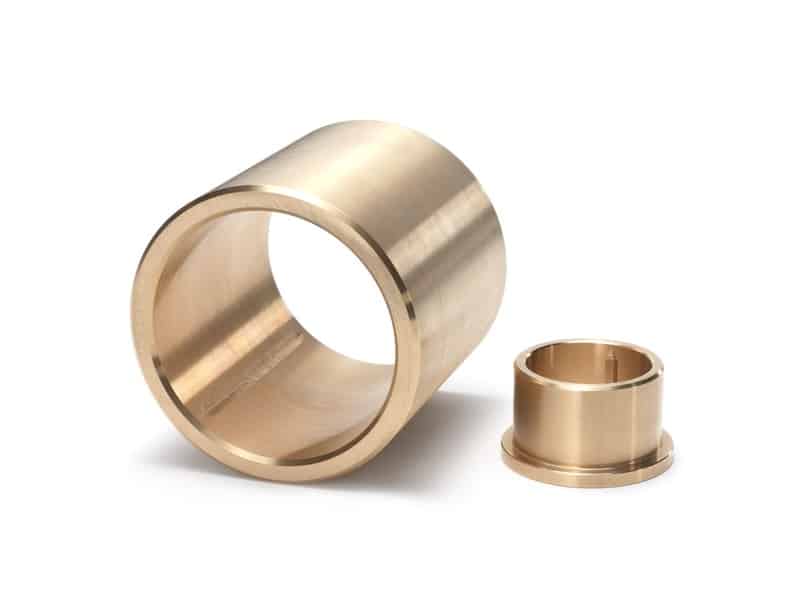
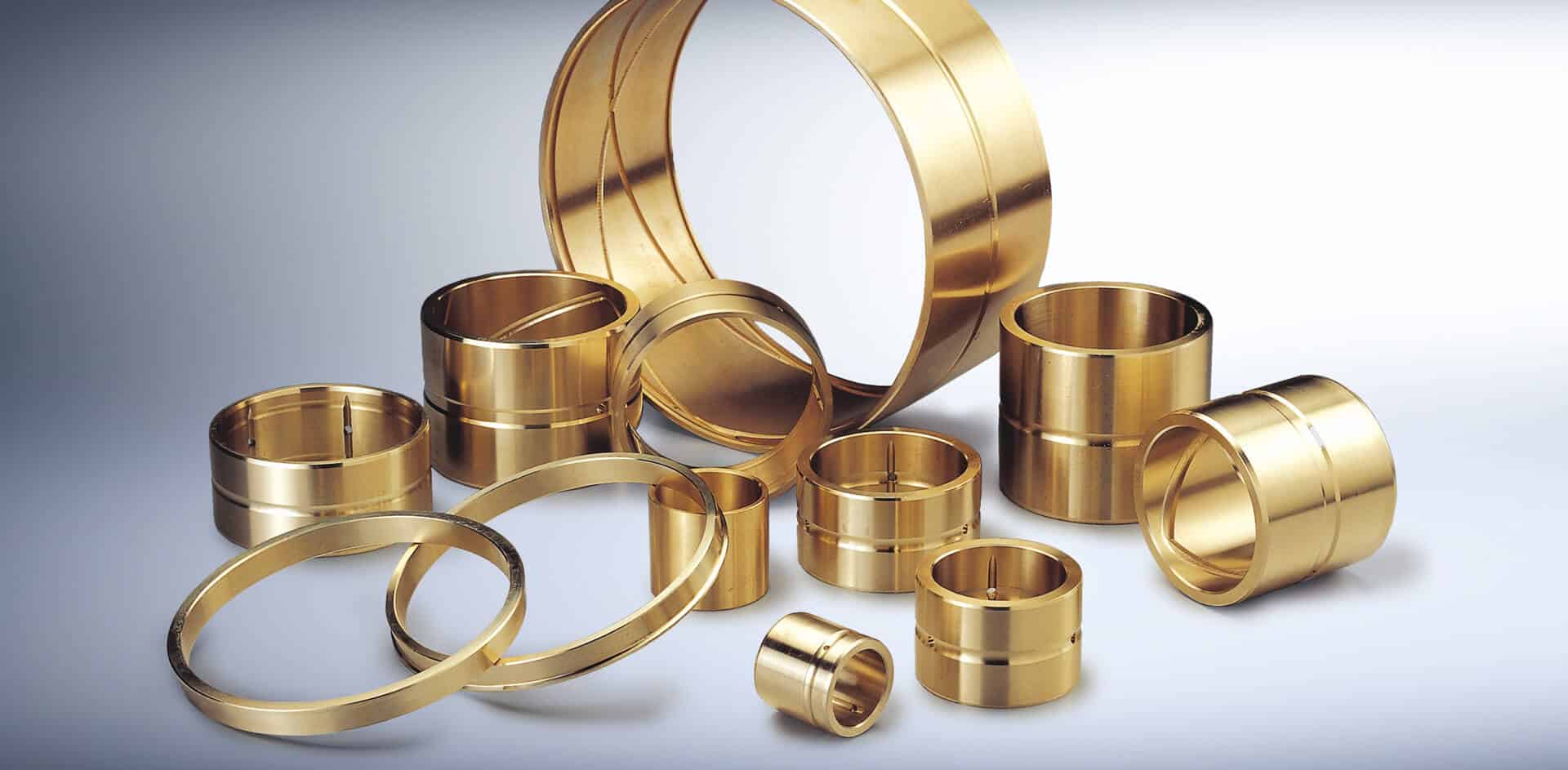
Project Description
Centrifugal Casting Projects
Self-lubricating Bronze Bearing Solutions
CNC Machining Parts Online – Custom CNC Parts, Online CNC Machining Services for Custom Parts, And Production Parts. China CNC Machining Prototype, Custom Parts & Rapid Prototyping. Order Status Tracking. Brass, Bronze & Copper Alloys, Green Alloys & Aluminum Bronze Bearing Manufacturing From China. Our wide range of aluminum alloys bushing and high precision machining of bushing. Continuous casting bushing, bearings consist of a support structure cast from one of four available high-quality bronze alloys.
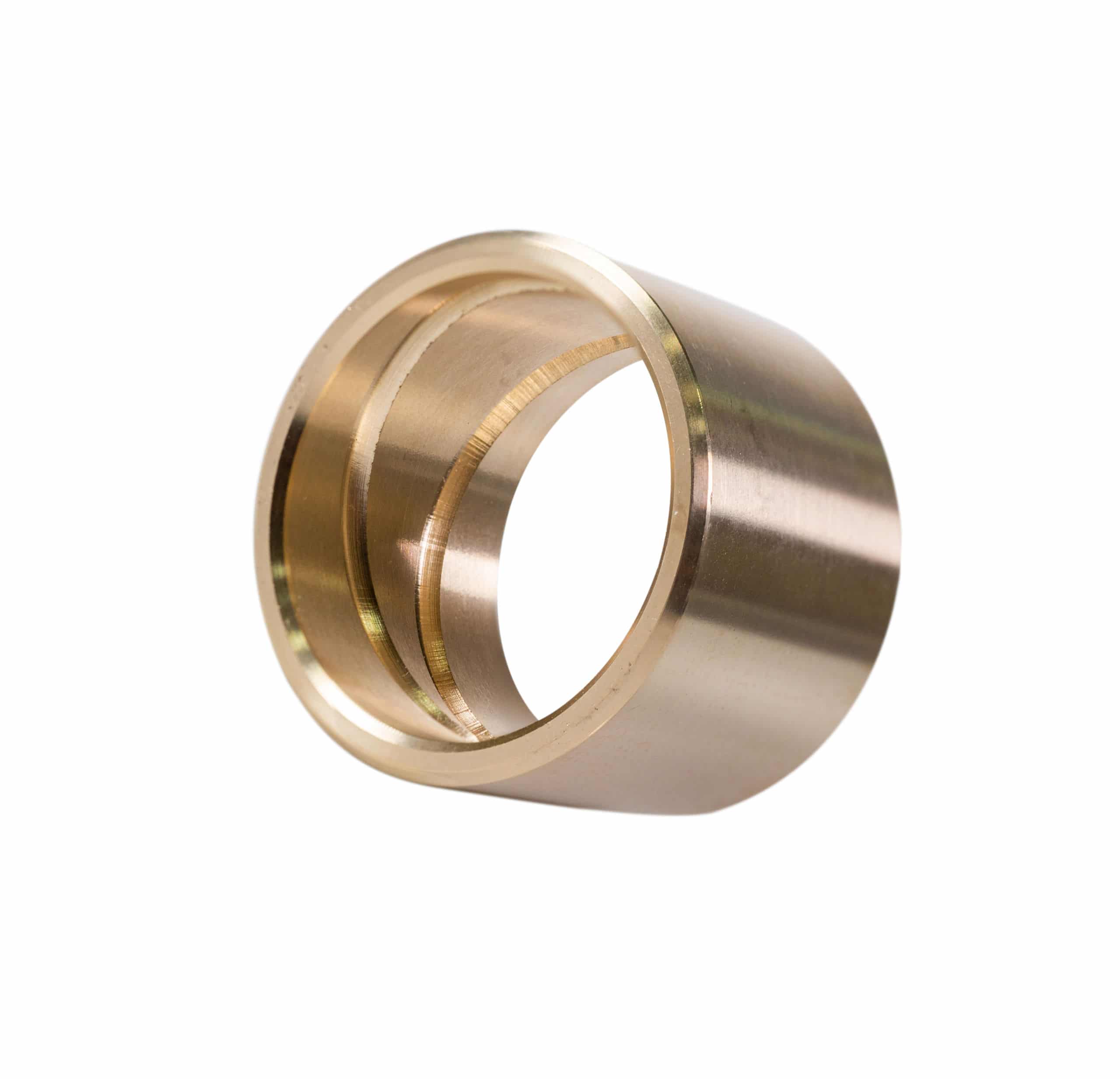

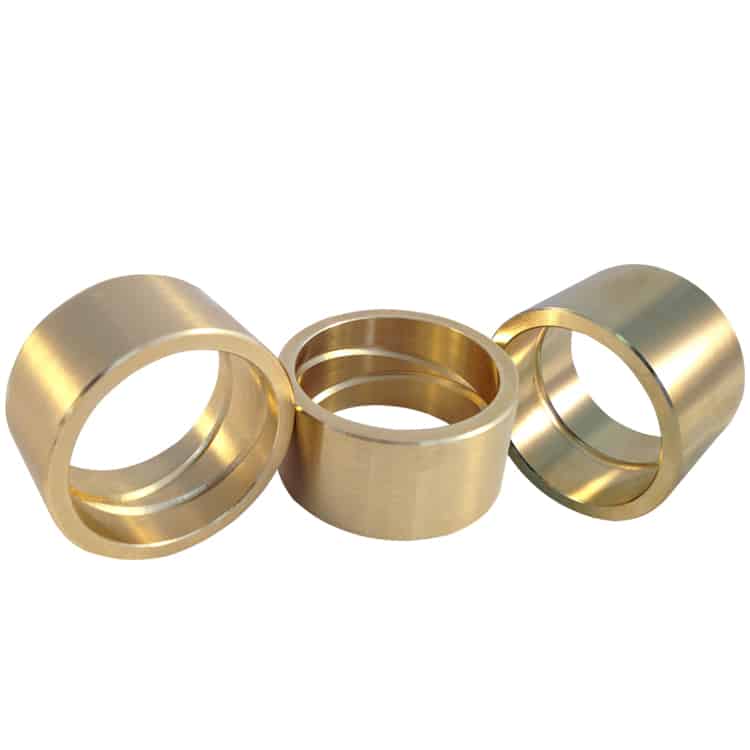
Centrifugal Casting Bronze Bearing
Centrifugal casting is a popular method used for manufacturing parts from copper-based alloys like bronze, brass, and copper itself. This process is favored for its ability to produce parts with superior mechanical properties and minimal impurities.
Here’s a general overview of how a manufacturing company might advertise its services:
“We specialize in providing copper alloy bars, plates, and parts designed for a variety of manufacturing and machining needs. Our expertise in centrifugal cast bronze, brass, and copper alloys can save you valuable time and money in research, design, and production costs.
Using the centrifugal casting process, we produce high-quality cylindrical parts including bearings, bushings, tubes, and other components. These cast parts are known for their density, uniformity, and superior mechanical properties that other casting methods may not consistently provide.
Our team of specialists is equipped to handle all types of copper alloys, including various types of bronze and brass. We offer a range of services including casting, machining, and finishing to meet all your manufacturing needs. With our services, you can expect to reduce the time spent in research, design, and production, thereby lowering your overall costs.”
Remember, when choosing a manufacturing partner, it’s important to consider factors such as their expertise, the quality of their products, their turnaround time, and their customer service.
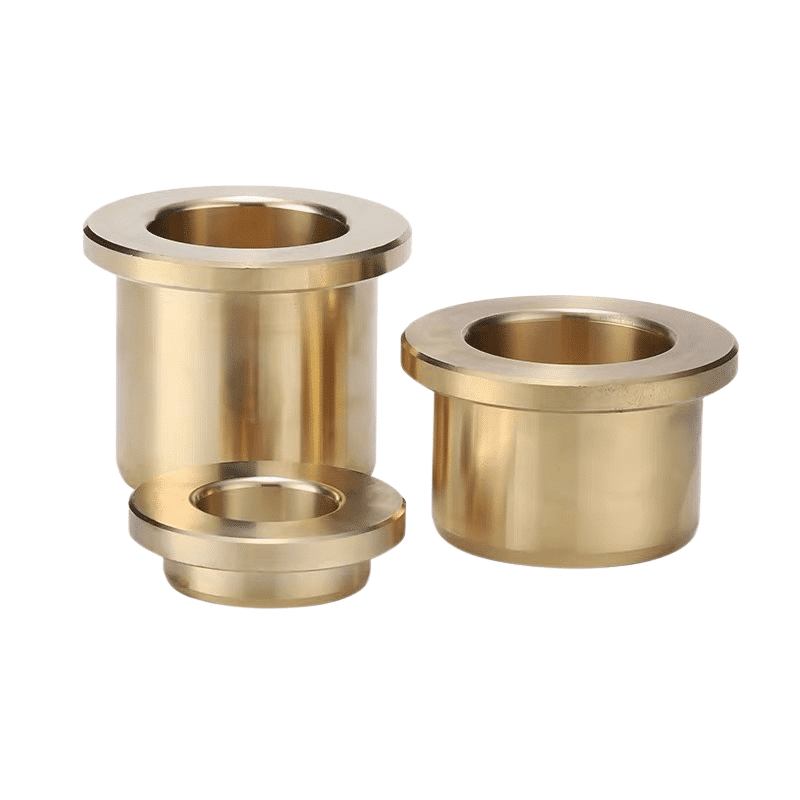

Centrifugal casting is a method of casting metal parts that involves the use of centrifugal force. It was developed around 1850 for the manufacturing of artillery and railway wheels. Today, it is widely used in various industries, including the manufacturing of bushings or bearings from materials like bronze.
The process begins by heating bronze to its melting point and then pouring it into a rotating mold. The centrifugal force generated by the rotation drives the molten bronze towards the mold’s walls, creating a uniform and dense casting. The impurities, being lighter, are forced towards the center and can be easily removed once the casting is complete. This is a key advantage of centrifugal casting, as it tends to produce parts with superior metallurgical properties compared to other casting methods.
When creating a bronze bushing or bearing using the centrifugal casting method, the process may be as follows:
-
Melting: The bronze alloy is melted in a furnace to a specific temperature. The alloy composition can be adjusted to achieve the desired properties in the final product, such as hardness, strength, or resistance to wear and corrosion.
-
Pouring: The molten bronze is poured into a preheated and rotating mold. The mold can be made of different materials, such as sand or metal, depending on the desired surface finish and dimensional accuracy of the casting.
-
Cooling: As the mold rotates, the bronze solidifies from the outer wall towards the center, creating a dense and uniform structure. The mold continues to rotate during the cooling process to ensure even solidification.
-
Removal and finishing: Once the bronze is completely solidified, the casting is removed from the mold. It may require further machining or finishing operations to achieve the final dimensions and surface finish.
-
Inspection: The final bushing or bearing is inspected for defects and to ensure it meets the required specifications. This can include visual inspection, dimensional checks, and various non-destructive testing methods.
The centrifugal casting method can produce high-quality bronze bushings and bearings with excellent mechanical properties and durability. It’s also a versatile method that can be used to create parts of various sizes and shapes.
Our Cast Bronze Bushings are machined from continuous cast C86300, C93200 (SAE 660) bronze for superior quality and performance.
Oil Groove. Machined cast bronze bearings offer technically and economically favorable bearings solutions.
| Technical Data | |||||
| Material | Brass | Bronze | Bronze | Bronze | Bronze |
| CuZn25Al5 | CuSn5Pb5Zn5 | CuAl10Ni5Fe5 | CuSn12 | CuSn10Pb10 | |
| Density | 8 | 8.9 | 7.8 | 8.9 | 8.9 |
| Yield pointN/mm2 | >450 | >90 | >260 | >150 | >100 |
| Tensile strengthN/mm2 | >750 | >200 | >600 | >260 | >210 |
| Elongation % | >12 | >15 | >10 | >8 | >8 |
| Hardness HB | >210 | >70 | >150 | >95 | >75 |
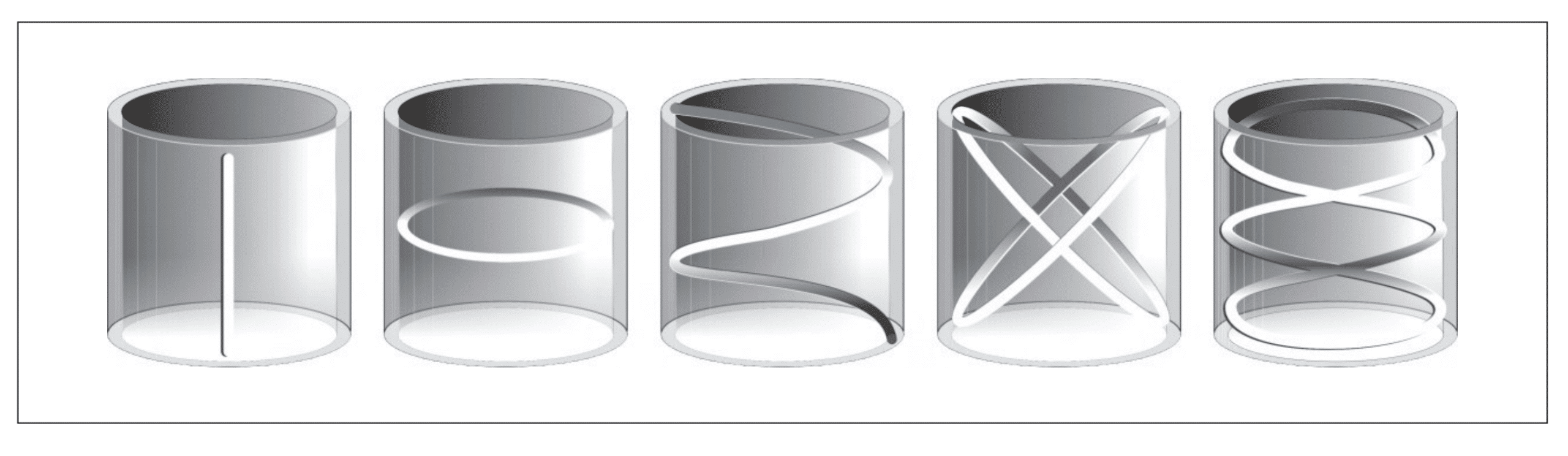
Centrifugal Casting
Centrifugal casting is widely used for manufacturing cylindrical parts like pipes, tubes, and bearings. The process involves pouring molten metal into a rotating mold. The centrifugal force pushes the metal against the mold walls and it solidifies from the outside in. This method is quite effective because it results in a component with fewer impurities and a denser grain structure, which in turn enhances the mechanical properties.
Centrifugally cast bronze bearings are widely sought after due to their superior durability and strength. The casting’s wall thickness is determined by the volume of the metal poured into the mold. However, due to the nature of the process, the interior diameter of the part is always circular.
Sand Casting
Sand casting, on the other hand, is more versatile in terms of the shapes and sizes of components that can be produced. It starts with creating a pattern in the shape of the desired part. This pattern is placed in a box, known as a flask, and surrounded with sand mixed with a binding agent that helps it retain its shape. After the mold has cured, the pattern is removed, leaving behind a hollow cavity in the shape of the part.
Molten bronze is then poured into this cavity, allowed to cool and solidify, forming the part. Once the metal has cooled and hardened, the sand mold is broken away. The resulting casting can be used as is, or may undergo further processes such as machining or surface finishing to achieve the desired specifications and finish.
Each of these methods has its advantages and is chosen based on the requirements of the final component – the size, shape, and desired physical and mechanical properties. For example, if a cylindrical component with superior mechanical properties is required, then centrifugal casting would be a good choice. For components with more complex shapes or larger sizes, sand casting may be more appropriate.
The cast bronze bushings basic features
Bronze bushing is a kind of high force brass bearing lubricated by groove gushing oil. The product has the function of traditional tin bronze bearing, because of the use of high force brass (ZCuZn24Al6), its HB hardness is doubled, so in low speed occasions, the life of the product can be twice longer than the general bronze sleeve, and its bearing pressure is large, can adapt to the use of heavy duty occasions. At present, the product is mainly used in excavator joints and large gear box.
Cast Bronze Bearing Characteristics
The so-called no-oil supply means no oiling or less oiling. The goal of our research is to ensure that the bearing can perform well under such conditions and prolong its service life as much as possible.
Standard Bronze Alloys C93200 & C86300 Standard material fulfills most application requirements
Cast Bronze Bushing Alloy
| Material code | (600#) |
Cast Bronze Bushing (600#S1) |
Cast Bronze Bushing (600#S2) |
Cast Bronze Bushing (600#S3) |
Cast Bronze Bushing (600#S4) |
Bushing (HT250) |
Bushing (Gcr15) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical composition | CuZn25Al5Mn3Fe3 | CuZn25Al5Mn3Fe3 | CuAl9Fe4Ni4Mn2 | CuSn5Pb5Zn5 | CuSn12 | HT250 | Gcr15 |
| Density(g/cm³) | 8.0 | 8.0 | 8.5 | 8.9 | 9.05 | 7.3 | 7.8 |
| Hardness (HB) | >210 | >250 | >150 | >70 | >80 | >190 | HRC>58 |
| Tensile strength (N/mm²) | >750 | >800 | >800 | >200 | >260 | >250 | >1500 |
| Elongation (%) | >12 | >8 | >15 | >10 | >8 | >5 | >15 |
| Linear expansion coefficient | 1.9 | 1.9 | 1.9 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.0 | 1.1 |
| Operating temperature(℃) | -40~+300 | -40~+150 | -40~+400 | -40~+400 | -40~+400 | -40~+400 | -40~+400 |
| Maximum dynamic load(N/mm²) | 100 | 120 | 150 | 60 | 70 | 80 | 200 |
| Maximum line speed(m/min) | 15 | 15 | 20 | 10 | 10 | 8 | 5 |
| Maximum PV value Lubricating (N/mm²*m/min) |
200 | 200 | 60 | 60 | 80 | 40 | 150 |
| Permanent compression deformation 300N/mm² |
<0.01 | <0.005 | <0.04 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.015 | <0.002 |

The feasibility of some standard cast bronze alloys bushing depends upon the dimensional and geometric requirements of each application! Density depends on the surrounding temperature and percentage of each alloy component in the material.
Standard Bronze Alloy Bushings
centrifugal casting bronze bushings
Casting copper alloy processing technology
1)Castability (castability)
It refers to the performance of metal materials that can obtain qualified castings by casting. Castability mainly includes fluidity, shrinkage and segregation.
Fluidity refers to the ability of liquid metal to fill the mold. Shrinkage refers to the degree of volume shrinkage of castings during solidification; Segregation refers to
In the process of cooling and solidification, the difference of crystallization order leads to the non-uniformity of chemical composition and structure in the metal.
(2) Malleability
It refers to that the shape of metal can not be changed under pressure. It includes the ability to
For casting, forging, rolling, stretching, extrusion and other processing, the malleability is mainly related to the chemical composition of metal materials.
(3) Machinability (machinability, machinability)
It refers to the degree of difficulty for metal materials to become qualified workpieces after being cut by cutting tools. Whether the machinability is good or bad is often used after machining
It is measured by the surface roughness of the part, the allowable cutting speed and the wear degree of the tool, which is related to the chemical composition of the metal material
Mechanical properties, thermal conductivity and work hardening degree are related to many factors. Hardness and toughness are usually used to determine the machinability
Roughly cut. Generally speaking, the higher the hardness of metal materials, the more difficult it is to cut; Although the hardness is not high, it is tough and difficult to cut
hard.
(4) Weldability (weldability)
It refers to the adaptability of metal materials to welding processing. It mainly refers to obtaining high-quality welding joint under certain welding process conditions
The ease of the head. It includes two aspects: one is bonding performance, that is, under certain welding process conditions, certain
The sensitivity of the metal to the formation of welding defects; The second is the service performance, that is, under certain welding process conditions. Certain metal welding
Applicability of grounding joint to service requirements
CuSn7Zn4Pb7 BRONZE BUSHING
Centrifugal casting is a common process used in the manufacturing of bronze sleeve bearings. In this context, you’ve mentioned the alloy CuSn7Zn4Pb7, which is a specific type of bronze known as leaded gunmetal or leaded bronze. This alloy is used in the production of bearings due to its excellent wear resistance and good machinability, largely attributed to the presence of lead.
Here’s a simplified breakdown of the process:
-
Melting: The CuSn7Zn4Pb7 alloy (composed of approximately 7% tin, 4% zinc, 7% lead, with the remainder being copper) is melted in a furnace until it reaches its liquid state.
-
Pouring: The molten alloy is poured into a spinning mold. This mold is rotated around its axis at a high speed. The speed is predetermined based on the desired characteristics of the final product.
-
Cooling: As the mold spins, the alloy cools and solidifies from the outside towards the center. This creates a dense, uniform structure with fewer impurities, as impurities and gases are pushed towards the center of the casting due to their lower density.
-
Demolding and Finishing: Once the alloy is fully cooled and solidified, the casting is removed from the mold. The bearing may then undergo further processes such as machining, grinding, or polishing to achieve the desired dimensions and surface finish.
-
Inspection: The final product is inspected for any defects and to ensure it meets the necessary specifications. This can include visual inspection, dimensional checks, and various non-destructive testing methods.
The finished product, a centrifugally cast bronze sleeve bearing made from the CuSn7Zn4Pb7 alloy, benefits from superior mechanical properties and enhanced durability. These bearings are commonly used in applications that require high load capacity and resistance to wear.
GZ-CuSn12-C Alloy BRONZE BUSHING
Centrifugal casting is a commonly used process in the production of bronze straight bearings. In this context, you’ve referred to the alloy GZ-CuSn12-C, a specific type of tin bronze. This alloy is favored in the manufacturing of bearings due to its excellent load carrying capacity, wear resistance, and good machining properties.
Let’s go through a simplified version of the process:
-
Melting: The GZ-CuSn12-C alloy (consisting of about 12% tin with the remainder being copper, and possibly minor amounts of other elements) is heated in a furnace until it reaches a molten state.
-
Pouring: The liquid alloy is poured into a rotating mold. This mold is spun around its axis at a specific speed, determined by the characteristics desired for the final product.
-
Cooling: As the mold rotates, the alloy cools and solidifies from the outside in. This results in a dense, uniform structure with minimal impurities. The lighter impurities and gases are forced towards the center due to the centrifugal force and can be removed easily.
-
Demolding and Finishing: Once the alloy has completely cooled and solidified, the casting is removed from the mold. The bearing may then undergo further machining or finishing operations to reach the desired dimensions and surface finish.
-
Inspection: The final bearing is inspected for any defects and to verify it meets the necessary specifications. This can include visual inspection, dimensional checks, and various non-destructive testing methods.
The finished product is a centrifugally cast bronze straight bearing made from the GZ-CuSn12-C alloy, noted for its superior load capacity and wear resistance. These bearings are typically used in high-load, high-wear applications.
When determining the size or calculating the service life of an application, like a bronze bearing for instance, several factors are taken into account:
-
Specific Load Limit (p [MPa] lim): This refers to the maximum load the bearing can handle per unit area without failure under specific operating conditions.
-
pU Factor ([MPa x m/s]): The pU factor is a parameter used to define the permissible speed-load characteristics of a bearing. It’s a product of the bearing load (p) and the sliding speed (U).
-
Mating Surface Roughness (Ra [µm]): This is a measure of the texture of the surface where the bearing will be installed. A smoother surface can reduce friction and wear, improving bearing performance and lifespan.
-
Mating Surface Material: The material of the mating surface can impact the bearing’s performance. Certain materials pair better with bronze bearings than others.
-
Temperature (T [°C]): Bearings often have to operate under varying temperature conditions. The operational temperature can affect the bearing’s lubrication, material properties, and overall performance.
-
Other Factors: This can include things like the design of the bearing and the housing material, the type and frequency of lubrication, the presence of dirt or contaminants, and other external influences.
All these parameters are considered when determining the right bearing size for an application or when calculating the expected service life of a bearing.
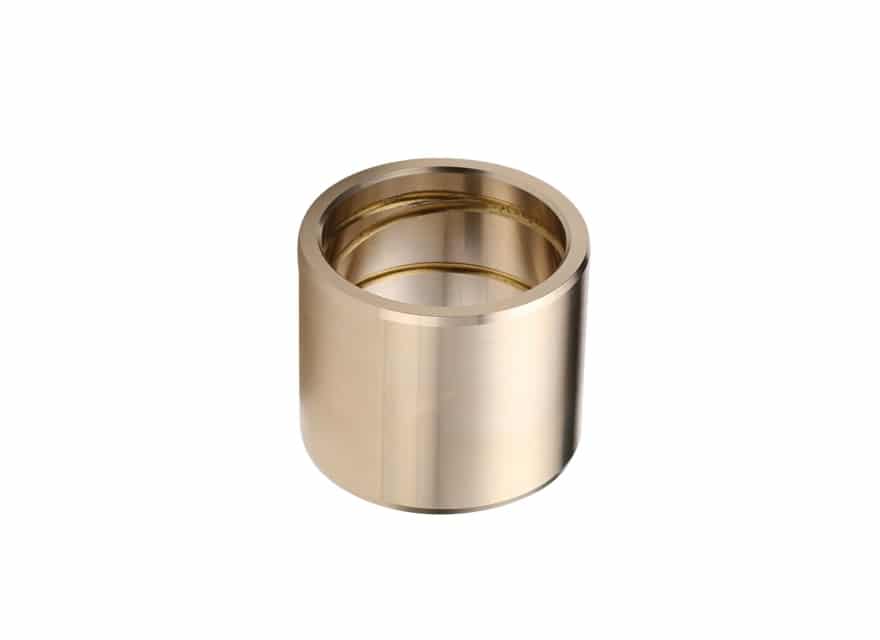
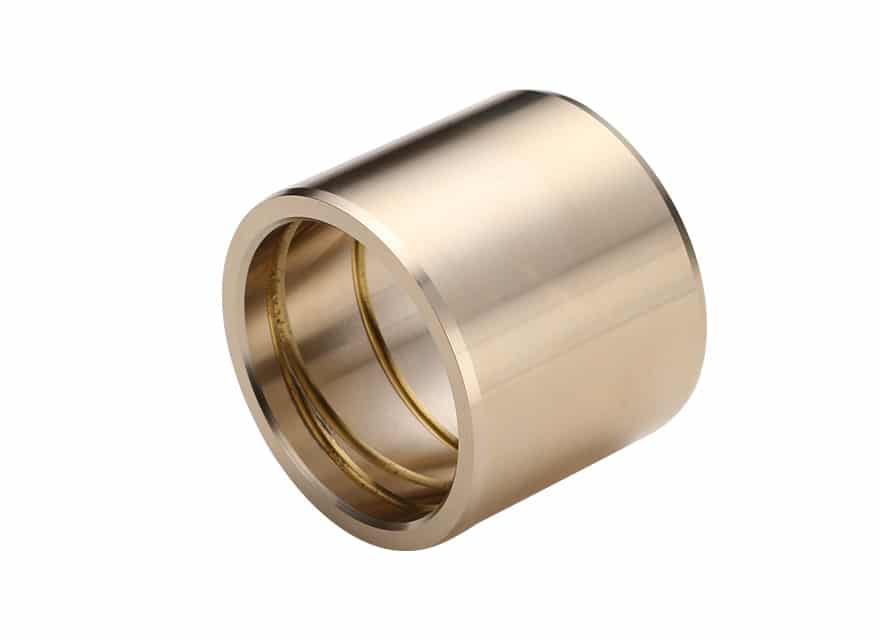
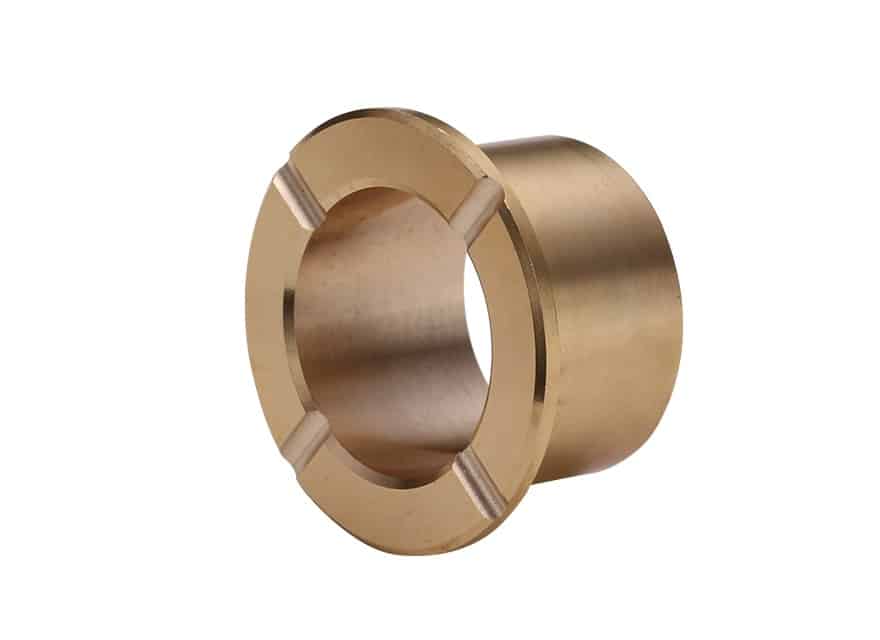



Cast Bronze Bushing Design Factors
The main parameters for determining the size or calculating the service life of your application..
In terms of purchasing, standard cast bearing sizes are often available for online sales. However, sizes can also be determined based on specific application operational data if standard sizes are not suitable. It’s worth noting that all cast bronze bearings are typically manufactured based on customer request and may not be immediately available ex-stock. This means they are made to order, and may not be readily available for immediate shipment.
Forms and Dimensions
The promise of cast bronze bushing high quality, meet your requirement.
Manganese Bronze Bushing Made To Order
Small minimum order value & quantity, fast delivery.






